Abstract
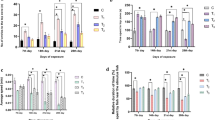
The objective of this study was to evaluate the effect of anthropogenic pollution on DNA damage and the fatty acid profile of the bottom dweller fish (Cirrhinus mrigala), collected from the River Chenab, in order to assess the effect of the toxicants on the quality of the fish meat. The levels of Cd, Hg, Cu, Mn, Zn, Pb, Cr and Sn and of phenols from this river were significantly higher than the permissible limits set by the USEPA. Comet assays showed DNA damage in Cirrhinus mrigala collected from three different sampling sites in the polluted area of the river. Significant differences were observed for DNA damage through comet assay in fish collected from polluted compared to control sites. No significant differences were observed for DNA damage between farmed and fish collected from upstream. The micronucleus assay showed similar trends. Fish from the highly polluted sites showed less number of fatty acids and more saturated fatty acids in their meat compared to fish from less polluted areas. Several fatty acids were missing in fish with higher levels of DNA in comet tail and micronucleus induction. Long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids, eicosapentaenoic acid (20:5n-3) was found missing in the fish from polluted environment while it was found in considerable amount in farmed fish 7.8±0.4%. Docosahexaenoic acid (22:6n-3) also showed significant differences as 0.1±0.0 and 7.0±0.1% respectively, in wild polluted and farmed fishes.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ackman R G. 1967. Characteristics of the fatty acid composition and biochemistry of some fresh-water fish oils and lipids in comparison with marine oils and lipids. Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology, 22 (3): 907–922.
Alink G M, Quik J T K, Penders E J M, Spenkelink A, Rotteveel S G P, Maasc J L, Hoogenboezem W. 2007. Genotoxic effects in the Eastern mudminnow (Umbra pygmaea L.) after exposure to Rhine water, as assessed by use of the SCE and Comet assays: a comparison between 1978 and 2005. Mutation Research / Genetic Toxicology and Environmental Mutagenesis, 631 (2): 93–100.
Boyd, E. C. 1981. Water Quality in Warm Water Fish Ponds. 2nd edn. Craftmaster Printers Inc. Opelika, Albama. 354p
Burger J, Gochfeld M. 2005. Heavy metals in commercial fish in New Jersey. Environ mental Res earch, 99 (3): 403–412.
Burr M L, Fehily A M, Gilbert J F, Rogers S, Holliday R M, Sweetnam P M, Elwood P C, Deadman N M. 1989. Effects of changes in fat, fish, and fibre intakes on death and myocardial reinfarction: diet and reinfarction trial (DART). Lancet, 2: 757–757.
Dhawan A, Bajpayee M, Pandey A K, Parmar D. 2009. Protocol for the single cell gel electrophoresis / comet assay for rapid genotoxicity assessment. Developmental Toxicology Division Industrial Toxicology Research Centre Marg, Lucknow 226001 U. P. India, Retrieved September 21, 2015 from http//www.cometassayindia.org/Protocol%20for%20Comet%20Assay.pdf.
Galindo B A, Troilo G, Cólus I M S, Martinez C B R, Sofia S H. 2010. Genotoxic effects of Aluminum on the Neotropical fish Prochilodus lineatus. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 212 (1-4): 419–428.
Hedayatifard M, Jamali Z. 2008. Evaluation of omega-3 fatty acids composition in Caspian Sea pike perch (Sander lucioperca L.). International Journal of Agriculture and Biology, 10: 235–235.
Hussain B, Mahboob S, Hassan M, Nadeem S, Sultana T. 2011. Effect of maturation degree on fatty acid profile of different tissues in wild and farmed rohu (Labeo rohita). Grasas Y Aceites, 62 (2): 206–212.
Kandemir S, Polat N. 2007. Seasonal variation of total lipid and total fatty acid in muscle and liver of Rainbow Trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss W., 1792) reared in Derbent Dam Lake. Turkish Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences, 7: 27–27.
Kiessling A, Pickova J, Johansson L, Åsgård T, Storebakken T, Kiessling K H. 2001. Changes in fatty acid composition in muscle and adipose tissue of farmed rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) in relation to ration and age. Food Chemistr y, 73 (3): 271–284.
Mahboob S, Al-Balwai H F A, Al-Misned F, Ahmad Z. 2014. Investigation on the Genotoxicity of Mercuric Chloride to freshwater Clarias gariepinus. Pakistan Veterinary Journal, 34 (1): 100–103.
Nhapi I, Wali U G, Uwonkunda B K, Nsengimana H, Banadda N, Kimwaga R. 2011. Assessment of water pollution levels in the Nyabugogo Catchment, Rwanda. The Open Environmental Engineering Journal, 4: 40–40.
Obiakor M O, Ezeonyejiaku C D, Ezenwelu C O, Ugochukwu G C. 2010. Aquatic genetic biomarkers of exposure and effect in Catfish (Clarias gariepinus, Burchell, 1822). American-Eur asian Journal of Toxicological Sciences, 2 (4): 196–202.
Pavlica M, Štambuk A, Malovic L, Mladinic M, Klobucar G I V. 2011. DNA integrity of chub erythrocytes (Squalius cephalus L.) as an indicator of pollution-related genotoxicity in the River Sava. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 1 77 (1-4): 85–94.
Pietripiana D, Modena M, Guidetti P, Falugi C, Vacchi M. 2002. Evaluating the genotoxic damage and hepatic tissue alterations in demersal fish species: a case study in the Ligurian Sea (NW-Mediterranean). Marine Pollution Bulletin, 44 (3): 238–243.
Polvi S M, Ackman R G. 1992. Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar) muscle lipids and their response to alternative dietary fatty acid sources. Journal of Agriculture and Food Chemistry, 40 (6): 1001–1007.
Shahidi F, Boota J R. 1994. Seafoods: Chemistry, Processing Technology and Quality. Chapman and Hall, London. p. 3–9.
Swapna H C, Rai K R, Bhaskar N, Sachindra N M. 2010. Lipid classes and fatty acid profile of selected Indian fresh water fishes. Journal of Food Science and Technology, 47 (4): 394–400.
Tocher D R, Bell J G, McGhee F, Dick J R, Fonseca-Madrigal J. 2003. Effects of dietary lipid level and vegetable oil on fatty acid metabolism in Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.) over the whole production cycle. Fish Physiology and Biochemistry, 29 (3): 193–209.
USEPA. 1999. National recommended water quality criteriacorrection. EPA 822/Z-99-001. USEPA, Washington, DC.
Van Der Oost R, Beyer J, Vermeulen N P E. 2003. Fish bioaccumulation and biomarkers in environmental risk assessment: a review. Environmental Toxicology and Pharmacology, 13 (2): 57–149.
Villela I V, de Oliveira I M, da Silva J, Henriques J A P. 2006. DNA damage and repair in haemolymph cells of golden mussel (Limnoperna fortunei) exposed to environmental contaminants. Mutation Research / Genetic Toxicology and Environmental Mutagenesis, 605 (1-2): 78–86.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by the Research Group Project of Deanship of Scientific Research at King Saud University (No. RG-1435-012)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hussain, B., Sultana, T., Sultana, S. et al. Effect of pollution on DNA damage and essential fatty acid profile in Cirrhinus mrigala from River Chenab. Chin. J. Ocean. Limnol. 35, 572–579 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00343-017-5304-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00343-017-5304-5